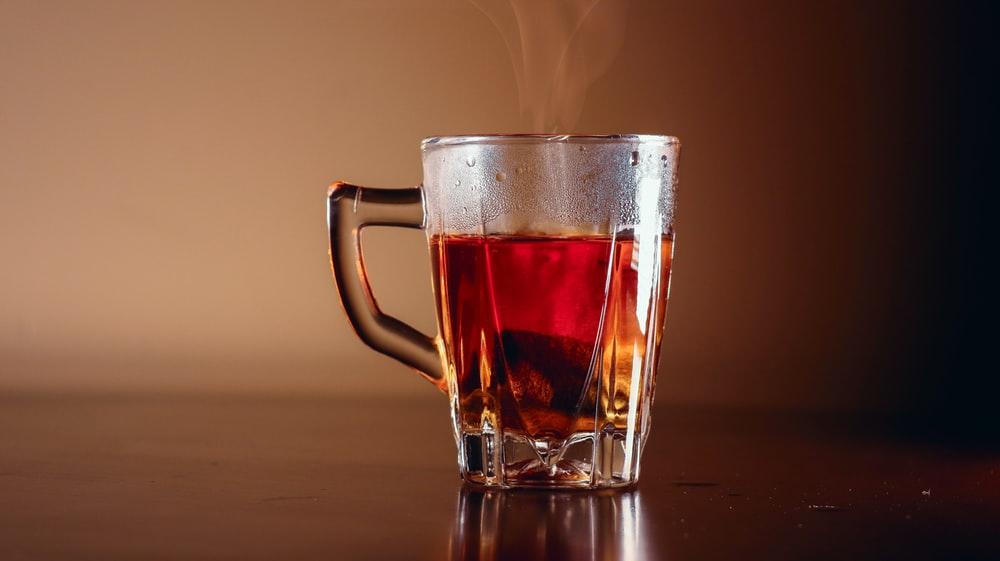
Numerous children are treated for burn injuries every year. Some of these injuries are sustained by scalding liquids like tea or hot water. With their inherent curiosity about everything in their surroundings, as well as their new independence, children younger than five years are the most susceptible to enduring burn injuries. These burns are not linked to fire but are as a result of scalding from very hot or boiling liquids. Instances like these happen more often than fire-related burns. If the child survives such an incident, more severe injuries can necessitate a lifetime of medical attention and rehabilitation.
How Can Burn Injuries Be Prevented?
Any burns that occur in children are profoundly unsettling. However, they can be prevented by practicing vigilance and monitoring from caregivers and parents. Children can sustain burns in various ways, but in most cases, they could have been prevented before happening. There are a few methods of making your home safer, but it is equally important to remind your children constantly of the danger of being near boiling liquids or flames. It must be reinforced daily.
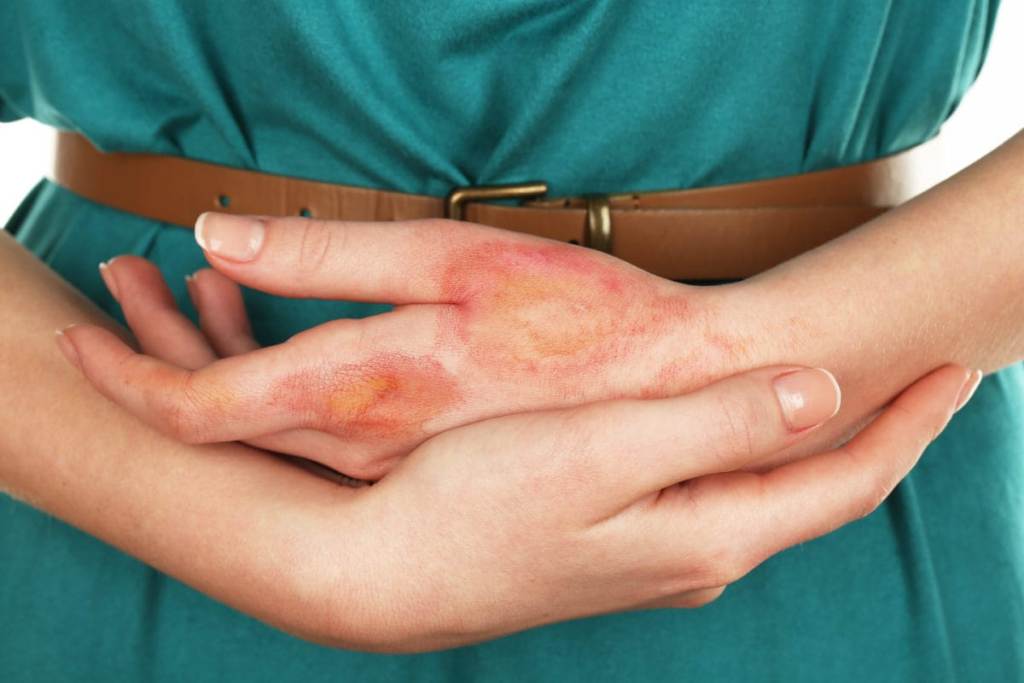
Preventative Measures:
- Remain vigilant with your children around candles, heaters, stoves or other open flames from paraffin lamps, braais, coal fires, portable stoves, etc.
- Pot handles must be turned towards the back of your stove.
- Hot liquids and foods must be placed in the center of the table.
- Before bathing your child, always test the temperature of the bathwater with your elbow. Read more parenting tips at tinytribes.co.
- Place kettles with cords out of reach at the back of the table or counter.
- Start teaching your child from a young age about the difference between cold and hot taps.
- Never overload power points and run electrical wires underneath carpets.
- Use safety plugs to cover unused power outlets.
- Never cook while holding your child.
- Always extinguish coal and wood fires immediately with water and oil, paraffin or petrol fires with a fire extinguisher or sand when you’ve finished using them.
Simple First-Aid Steps In Case Of A Child Being Burned:
- Immediately remove the child from the danger source.
- Cool the burn under cold water for an extended period.
- Protect the injury with plastic wrap or a clean cloth.
- Immediately seek advice from emergency services or a medical professional.
Degrees Of Burns
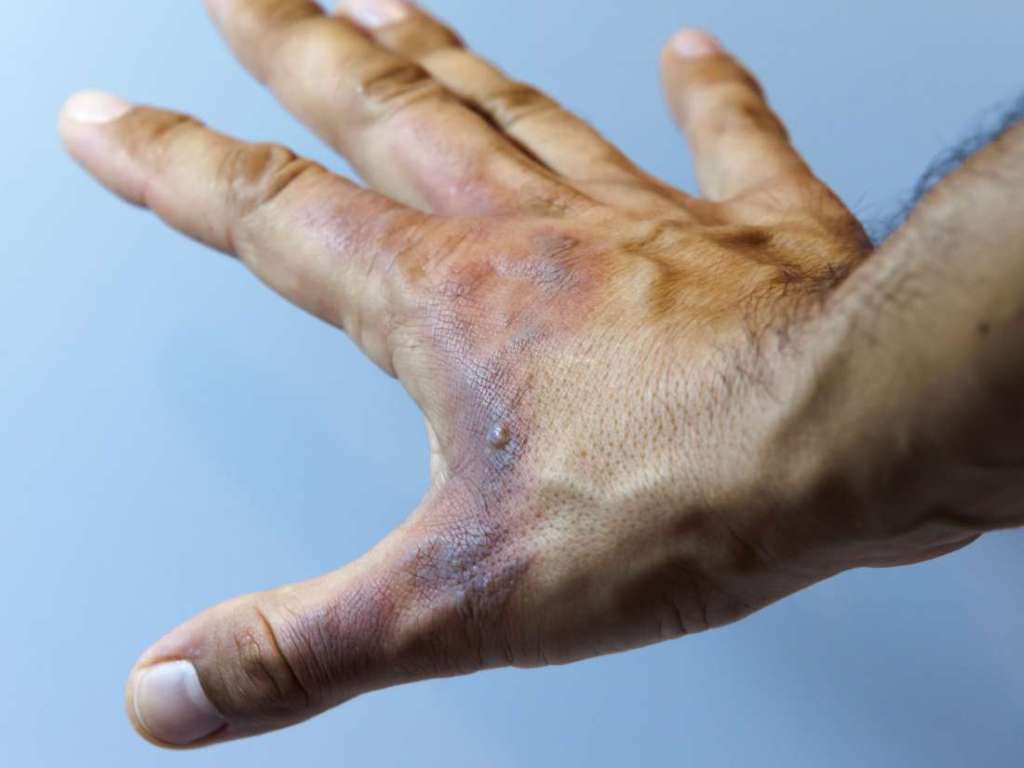
- First degree – Red skin with no blisters and heals without scarring.
- Second degree – Full or partial thickening of the skin and blisters. Full-thickness burns may necessitate skin grafting for best healing.
- Third-degree – Thickening overall of the affected skin with white coloring. The burn has gone right through the skin.
Burn Injury Sources
- Thermal – can result from flame, explosions, hot liquids, and touching hot materials such as heated colas or glass.
- Chemical – caused by strongly alkaline or acidic substances and necessitate special care to discontinue injury to the skin.
- Electrical – caused by electricity and must be assessed by a doctor or medical professional even if they appear fine since they can’t be accurately ascertained just through external appearance.






